The ratio of accounts receivable turnover shows how well a business in India turns its credit sales into cash collections during a certain time frame. This displays the typical rate at which money owed from clients is gathered in one quarter or year. Trade receivables, commonly known as accounts receivable, are situations where customers have been given credit for goods or services that they still need to pay after an accounting period ends.
This is a good statistic to find out if a company has the correct credit and collection policies set up to make sure it gets cash in on time. The importance of the ratio also holds under Indian tax law, so businesses must assess its impact with care. This article looks into how this ratio can be calculated, what it means about forecasting cash flow and managing working capital; also pointing out opportunities that may come up in quarterly results analysis for better financial understanding.
The net credit sales display how many accounts receivable are collected during a particular time frame, and the percentage of AR turnover signifies how effectively a business manages its invoicing assortment process. If the number is high, it may mean that funding is given quickly; whereas a low turnover value might hint at delayed customer payments. To compute the AR turnover ratio, we need to divide all net credit product sales in one quarter by the average daily accounts receivable balance. The formula below shows the average number of times the company collected payment for its receivables throughout its course.
Use this key formula:
AR Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
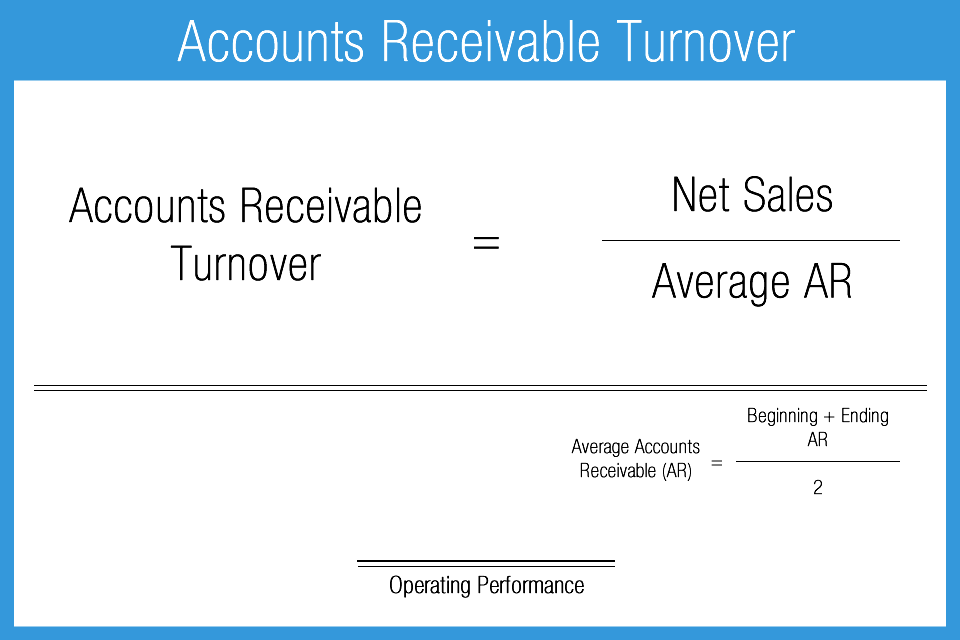
The AR turnover ratio is a critical measure telling us how good consumers are at getting paid. A decrease in the ratio might suggest slower payments or possible bad debts being formed. On the other hand, if this ratio goes up it could indicate better collection. The AR turnover ratio is a great way to understand how well you are managing and getting back money from accounts receivable. It can be even more helpful when used along with days sales outstanding, as it provides extra information about the risk involved in your AR.
In India, where credit is readily available, it becomes very important to handle accounts receivable efficiently. The next two main factors explain why the AR turnover ratio holds such significance:
1. Initially and most importantly, a solid ratio indicates that a business can gather outstanding debts swiftly. This ensures steady cash flow which assists in the smoother operation of businesses and lessens the requirement for external financing. The stream aids in maintaining inventory at par with demand. Consequently, there is a decrease in storage expenses and an increase in your negotiation power with suppliers due to the ability to make large purchases.
2. Changes in the timing of collections can also affect finances. When cycles are longer, it reduces liquidity and may require expensive borrowing. However, if we have fast receivables it can create its own set of troubles like hurried choices or a tense bond with clients. So, an even turnover rate displays the caution, steadiness and future-focused approach that is vital for any operation to prosper on a lasting basis.
3. One way to gauge credit risk is by looking at how quickly accounts receivable turn into cold hard cash. If things start moving slower than usual, it could mean there's a higher chance of not getting paid for your bills. That kind of situation might make businesses step up their game in evaluating whom they give credit to or consider ways to protect what they're owed.
The AR turnover ratio shows how efficiently a business collects payment for credit sales according to Indian Accounting Standards. These standards say that companies need to record the correct amounts they have billed their clients and also keep track of what is still owed by those who owe them money. The benchmarks assist in determining this crucial metric for assessing financial performance because they demand proper documentation of both credit transactions as well as subsequent debts due from customers or clients. At the same time, the ratio shows how good a company is at turning credit sales into cash within a certain period.
The AR turnover ratio demonstrates the speed at which a business changes credit sales into cash revenues. This vital number is affected by client credit conditions, norms in the industry, and other factors like the size and age of a company.
A higher ratio is usually a sign that the company has good methods for collecting, which makes the process of turning accounts receivable into cash faster. Things like macroeconomic headwinds, loose loan practices, or more emphasis on growth instead of cash flows might make collection time longer than usual. So, it isn't always an indication of issues when the ratio is lower. In-depth research considers aspects from the market and specific to companies.
In summary, to correctly understand the AR turnover ratio, you need to study the industry situation, loan conditions, and company profile. You should look at both numbers and non-numbers information to understand the performance of a specific company in this important area.
To enhance the AR rotation ratio, a business could apply credit regulations. If there are rules about creditworthiness, clear standards for determining who is creditworthy should be established. Also, if systematic procedures for collection have been detailed, businesses need to organize and execute them properly. This may help to improve the speed at which debts are collected by offering discounts on payments made within specific timeframes. The use of latest technologies makes accumulation campaigns automated and keeps track of unpaid balances more swiftly. Regular communication with clients helps to handle buildup concerns and answer any questions quickly. By managing their AR rotation ratio, businesses in India can achieve sustainable financial growth, improved cash flows, and maximum accumulations.
For businesses in India, the percentage of accounts receivable turnover reveals how well they handle their cash flow and are productive at raising capital. When businesses understand this number's meaning, know its calculation method plus what range can be seen as good or bad performance - then these numbers become useful guides for making smarter choices about credit collection/assortment strategies. Do not forget! Always use a modification approach; the goal always remains the same: to guarantee profitable accumulations while not blocking transaction development.
1. What information do I need to calculate the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
You require two numbers: net credit sales and average accounts receivable. Net credit sales signify the sum of all your credit sales minus returns and allowances.
2. What's the formula for the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
The formula is: Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
3. Is a higher or lower Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio better?
A bigger ratio normally suggests that a company is able to gather its receivables quickly and has an effective credit strategy. But, if the ratio becomes very high, it could mean the credit terms are too strict and this restricts sales.
4. Can I calculate the average collection period from the Turnover Ratio?
Totally! By dividing 365 by the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, you can find out how many days it takes to collect your accounts receivable on average.
5. Are there any limitations to using the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
This ratio does not take into account the credit quality of customers. A company may have a high turnover ratio because it gives very short credit terms, however, this can also result in increased bad debt.